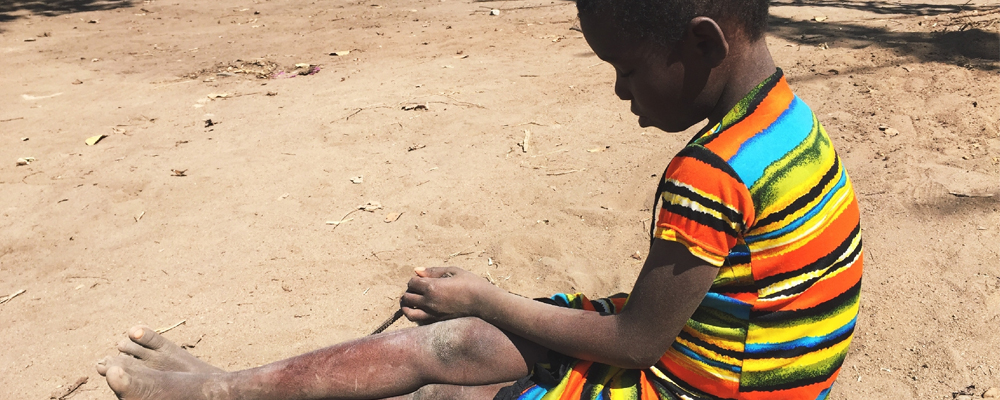
The poverty is the state in which an individual or group cannot meet basic human needs to maintain a minimum level of quality of life. Lack of income, employment, education, access to health or decent housing are some of the characteristics of this condition.
On the other hand, inequality refers to the unfair or unequal distribution of resources among various people or groups, caused by social, gender, ethnic, religious or other discrimination.
In this way, when speaking specifically of poverty, one speaks of the lack of some resource, generally economic, to maintain a dignified living condition. In the case of inequality, this refers to the way in which resources are distributed.
Difference between Poverty and Inequality
Both situations are complementary, but they do not necessarily present themselves at the same level. There can be a lot of inequality in a society without there being a lot of poverty and vice versa.
What is Poverty?
The poverty refers to a state in which a person or group of people cannot meet basic needs that maintain a viable level of socio – economic life. In conditions of poverty, people are unable to participate in social life and make social contributions.
In this way, poverty promotes a vicious cycle. The lack of employment, education, as well as conditions that allow the socioeconomic development of the individual and the community, limit the possibilities of people to leave this state.
According to the United Nations, a person is in a state of poverty when he does not have access to means that guarantee the satisfaction of certain basic needs.
Lack of resources, discrimination and various forms of inequality, infrastructure problems, wars and conflicts are some of the most common causes of poverty in different regions.
In general, when we talk about poverty in a country, compared to other countries, or an individual compared to their fellow citizens, we talk about poverty in socio-economic terms. In other words, poverty in this sense is focused on those populations that are in the lowest social stratum.
Characteristics of Poverty
- It expresses the lack of something that is necessary.
- In conditions of poverty there is a vicious cycle.
- Limited or nonexistent basic services.
- There are nutrition problems.
- Low schooling.
- It carries health problems (including a short life expectancy).
- It generates social violence, isolation and discrimination.
Causes of Poverty
- Socioeconomic, gender, ethnic inequality, etc.
- Difficulty of access to basic resources such as food, drinking water, housing and health.
- Educational problems.
- Wars and armed conflicts.
- Colonialism and slavery.
- Lack of employment.
- Infrastructure problems (regional and national).
- Scarcity of material resources (for example, agricultural and natural).
What is Inequality?
The inequality refers to an imbalance or uneven distribution of a resource between two or more agents.
When there is inequality, there is a difference between what someone owns and what they have access to, compared to what another person owns or has access to. Likewise, inequality can span the entire social spectrum and not just populations with the lowest economic level.
Inequality covers several interrelated aspects, which can be economic, social, gender, educational, religious, etc.
Inequality shares with poverty the fact that it can sustain or promote a vicious cycle. It is very difficult to get out of a situation where resources are unevenly distributed.
Characteristics of inequality
- Resources or income are unevenly distributed.
- Be part of and promote a vicious cycle.
- There is social, gender, ethnic discrimination, etc.
- One person or group has little access to opportunities.
- Limits participation in the social and political life of a group.
Causes of inequality
- Unequal distribution of the wealth of a country.
- Political and social problems.
- Wars and armed conflicts.
- Being in a state of inequality favors its perpetuity.
- Lack of access to education.
- Discrimination based on gender, religion, ethnic origin, sexual preference, etc.