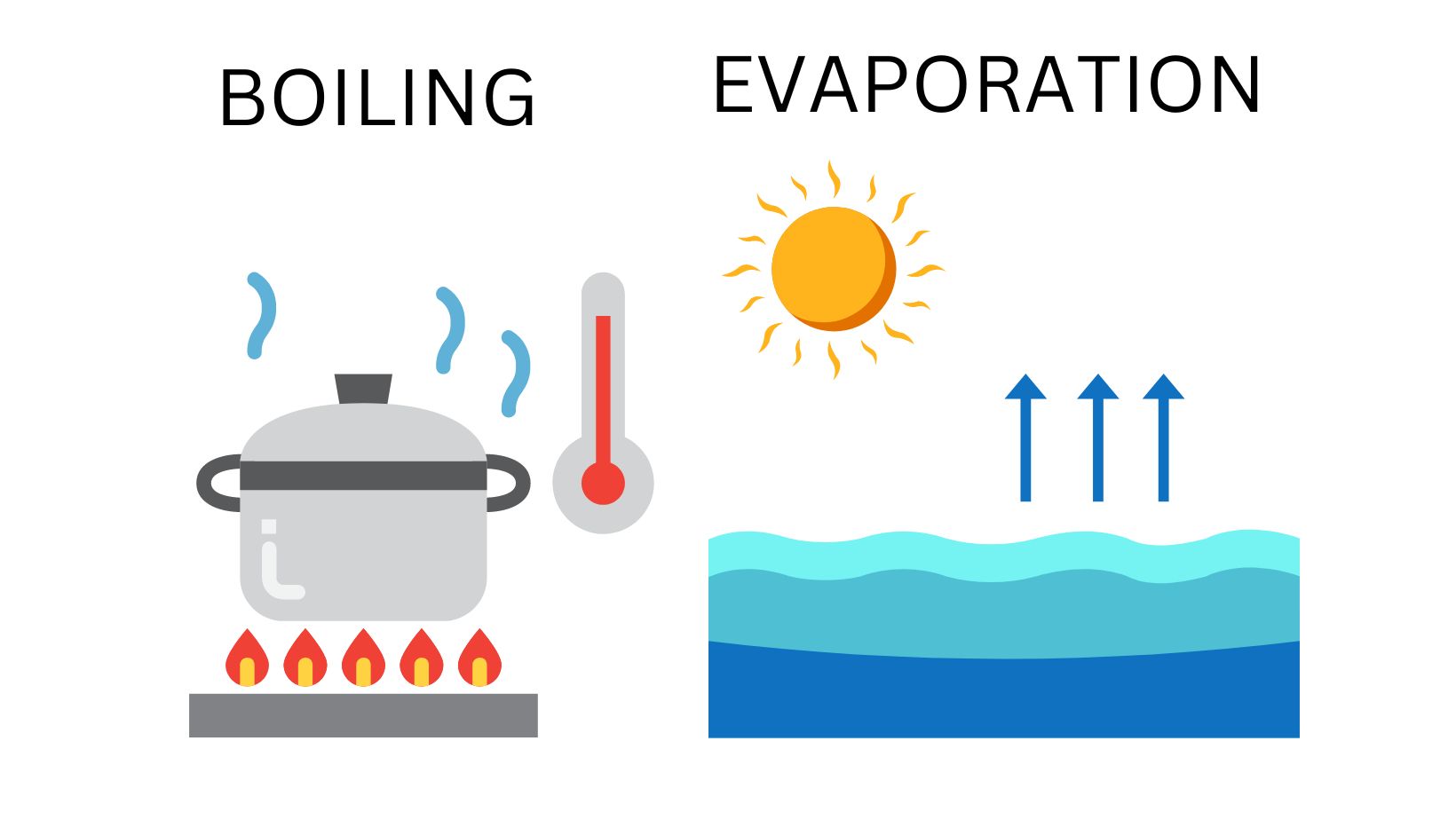
The main difference between evaporation and boiling is that evaporation considers the vaporization of the liquid at room temperature while boiling is the vaporization of the liquid when it is heated to its maximum boiling point.
What is the Difference between Evaporation and Boiling
The vaporization of the liquid takes place at room temperature in the evaporation process, while the vaporization of the liquid takes place at the boiling point of the liquid in the boiling process.
Evaporation could occur at any given temperature, while boiling occurs only at the given boiling point of the liquid, and the temperature required boiling the liquid remains constant throughout the entire boiling process.
The target surface molecules mainly throughout the evaporation process, so evaporation occurs mainly on the surface of liquids; on the other hand, boiling occurs during the entire boiling of the liquid.
When evaporation occurs in the bulk liquid body, the temperature of the liquid body tends to decrease; on the contrary, when boiling takes place in a bulk liquid body, the temperature tends to remain constant throughout the boiling process.
When the quality of the air present above the liquid remains unsaturated, the evaporation process continues.
On the other hand, when the pressure of the liquid present inside the boiling process remains equal to the external pressure of the boiling, the boiling process continues to take place. On evaporation, bubbles do not form; on the other hand, bubbles form when boiling.
In evaporation, the environment supplies energy to the reaction; rather, a primary energy source is required to carry out the boiling process.
Evaporation is considered the slow process; on the other hand, boiling is usually the quick process.
During evaporation, the temperature of the liquid is reduced, while the boiling temperature remains constant throughout the process.
Consequently, evaporation causes cooling of the liquid, while heat is formed as a result of boiling and does not because cooling of the liquid.
As the evaporation rate is directly dependent on the surface temperature, it means that a large surface area provides rapid evaporation of the liquid.
On the other hand, in boiling, the temperature does not increase any more from the boiling point of water, i.e. 100 degrees centigrade even though the continuous supply of heat is given.
What is Evaporation?
The term evaporation is defined as the method of escape of liquid molecules from the outside of a liquid at any given temperature is called evaporation.
The degree of evaporation of the liquid depends directly on its temperature, surface area and the amount of water vapor that exists in the surrounding air.
Evaporation is a spontaneous process that usually occurs at room temperature due to high-energy liquid molecules escaping into the surrounding air.
Molecules that are present in a liquid have a fixed amount of freedom to move and have different amounts of kinetic energies.
Therefore, molecules that have a greater amount of kinetic energy will have a greater affinity to escape to a gaseous state by overcoming the pressures and tensions that could hold the molecule back.
Usually, the molecules that are present on the surface of the liquid are normally the ones that evaporate and usually only need a small amount of energy to escape from the liquid.
Although some molecules with a smaller percentage of a number are present deeper in the liquid, they generally evaporate and pass through the surface of the liquid avoiding the collisions present in the liquid, showing that they possess a sufficient amount of kinetic energy.
When the quality of the air above the liquid remains unsaturated, the evaporation process continues to take place, which means that the air above the liquid should be able to provide accommodations for the incoming molecules of the liquid.
These accommodation molecules absorb thermal energy and then convert it into their kinetic energy.
What is Boiling?
The term boiling is considered as the method in which the liquid stage transforms into the gas phase at a given constant temperature.
The limit where the liquid turns into the gas phase at a given temperature and pressure is generally known as the “boiling point” 100°C is the normal atmospheric pressure of the boiling point of water.
When the liquid is heated, the molecules present within the liquid begin to absorb the thermal energy provided and increase their kinetic energy, which increases evaporation, which occurs while the air remains unsaturated.
However, when the pressure of the liquid present inside the boiling process remains equal to the external pressure of the boiling, then the boiling process continues.
The boiling process occurs only at the given boiling point of the liquid, and the temperature required boiling the liquid remains constant throughout the entire boiling process.