The difference between custom and tradition lies in the form of its manifestation, in its form of transmission, in the number of people who adopt it and the time it is considered as such. In this sense, the custom is associated with a daily routine or individual habit, acquired by particular inclinations of the character of each family or coexistence group, such as “Luis has the habit of eating toast for breakfast.”
Difference between Custom and Tradition
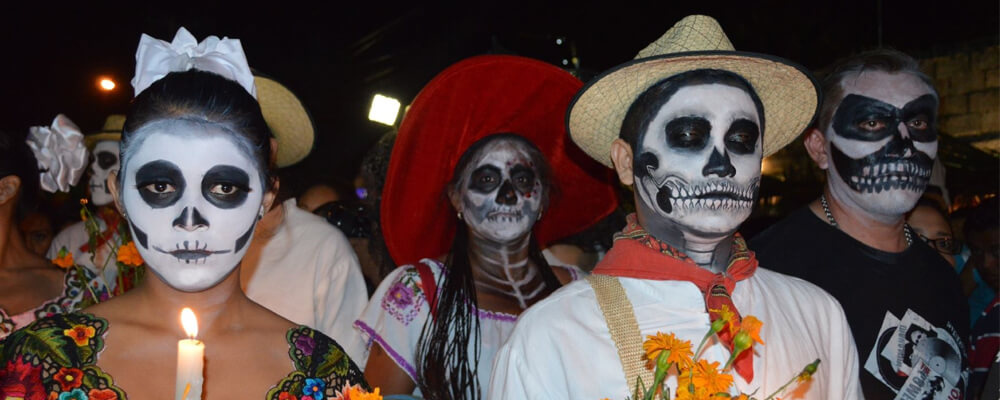
The tradition is customary with sociocultural roots that are particular to a group that also must be identified that way. The tradition is supported by historical antecedents that are transmitted from generation to generation, such as: “The Mexican literary tradition cannot ignore the poet Octavio Paz.”
Custom and tradition are part of the cultural identity that can be positional, community, regional, state, national or global.
Custom and tradition are also terms used synonymously, such as, “Catholics have the custom / tradition of putting up a tree as a decoration when they celebrate Christmas.”
In the example above, custom and tradition can be used synonymously because the Christmas tree is a particular symbol of families and communities, but also of Christian regions and families.
To differentiate a custom from a tradition, the form of transmission, historical antecedents, sociocultural elements, periodicity and the setting of important dates must be taken into account.
A custom, for example, if we consider the statement “lunch at one in the afternoon”, can be transmitted from generation to generation, the historical background can be associated with the definition of a time for lunch and it is desirable to do it every day.
Despite this, it is not considered a tradition because the elements are not particular to a community identified as such. In addition, the person would have to specify that he always has lunch at one in the afternoon or on a special day, and this last statement would have to have all the elements mentioned above.
On the other hand, the transmission of a tradition is perpetuated from generation to generation. Tradition maintains the memory of living historical antecedents by commemorating important dates, places or people at specific times, as well as being full of easily identifiable socio-cultural elements.
Folklore is the most reliable expression of tradition, since it groups together all the elements that compose it. Folklore expresses all the cultural forms inherited from previous generations, preserving in its customs and rites the cultural identity of a community.