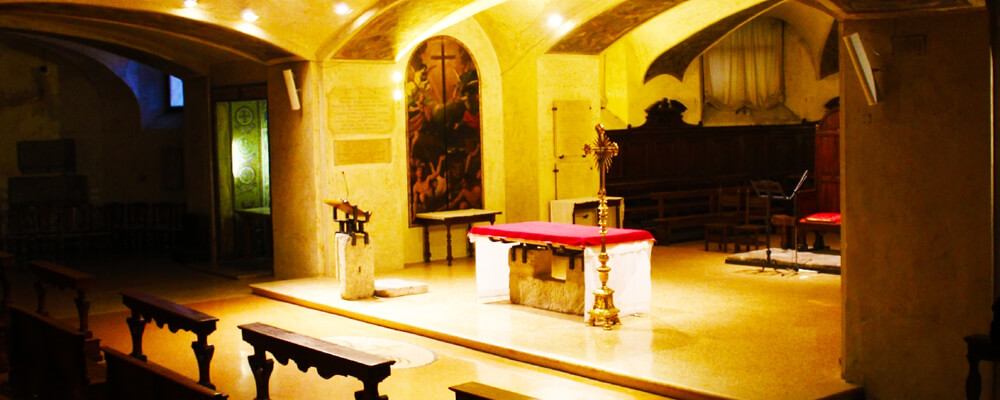
The difference between Christians and Catholics is that the term “Christians” includes all people, communities and churches that follow the teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. Therefore, Catholics are a specific type of Christians who embrace the interpretation of the Catholic Church.
Christianity is a spiritual current that has been interpreted in different ways, which has resulted in the existence of different churches, such as the Catholic Church, the Orthodox Church, the Anglican Church, the Coptic Church, the Calvinist Church, the Church Lutheran and Protestants in general.
Of all these confessions, Catholicism is perhaps the most numerous and widespread, so it has a very important referential weight.
What is the Difference between Christians and Catholics
Often times, some people use the term “Christians” to refer to the faithful of certain denominations of Protestant Christianity. However, this use is inaccurate, since it leaves out the other Christian confessions, which are numerous.
What is Christianity?
Christianity is a monotheistic religion founded on the teachings of Jesus of Nazareth, as well as on his life, death and resurrection. In this sense, Christianity welcomes various communities and churches such as Catholics, Orthodox, Protestants and other doctrines.
Origin of Christianity
The Christian religion originated in Judea in the 1st century AD and little by little it spread to Mesopotamia, Asia Minor, Syria, what today are the South Caucasus (Armenia, Georgia, Azerbaijan, etc.), Egypt, Ethiopia and the Empire Roman, from where it spread to everything in Europe today, especially after Emperor Constantine’s conversion to Christianity in the 4th century AD. C.
What is the Purpose of Christianity?
Christianity proposes the existence of a triune god, that is, the Holy Trinity, made up of God the Father, a merciful creator; God the Son, who died for the sins of the world and God the Holy Spirit, giver of life. The purpose of Christianity is to lead human beings to the love of the Father and to reconciliation with the brothers as a means to achieve eternal life.
Christian slopes or streams
More than types or categories of Christianity, what exists are slopes. The most important ones are:
Orthodox Church
It arises after the Eastern Schism of the year 1054. It is quite widespread in the countries of Eastern Europe and in some countries of the Middle East. The best known are the Russian and the Greek, but there is also the Syrian, the Lebanese, the Romanian, etc.
Protestant Churches
They arise after the schism promoted by Martin Luther in the 16th century, called the “Reformation”, whose purpose was to reform the Catholic Church which, by then, was facing a legitimacy crisis in various areas. Unlike the Catholic Church, they believe in the universal priesthood, that is, in the free interpretation of the scriptures and in the forgiveness of sins by justifying faith. Within Protestantism, the Lutheran, Anglican, Pentecostal, Evangelical, and Quakers churches, among others, stand out.
Christian hierarchy
The hierarchical structure in Christianity can vary according to its aspect. For example, in the Catholic Church, the structure is centralized and rests with the Pope, while in the Protestant Church, the hierarchy is decentralized and authority rests on the pastors, reverends or priests.
Holy book of Christians
The other confessions use the Alexandrian canon, although they organize it differently and may include some additional texts, such as Psalm 151.
The fundamental text of Christianity is the Bible. However, each Church is governed by a different version, which may include more or fewer books.
For example, the Catholic and Orthodox Church are governed by the Alexandrian canon, the 1970s or Septuagint Bible, while the Protestants are governed by the Hebrew canon, which excludes deuterocanonical books.
Doctrinal foundations of Christianity
- In general, all Christians confess the Apostles’ Creed:
- They believe in a God the Father, creator of the universe.
- Create a God the Son, Jesus, who became man, died, and rose again.
- They believe in the Holy Spirit, the giver of life.
- They believe in the second coming of Jesus.
- They believe in the Last Judgment.
- They believe in the forgiveness of sins.
- They believe in the resurrection of the dead.
However, each Church interprets and expresses these elements differently.
What is Catholicism?
The Catholic Church is a community of Christian faithful who gather around the figure of the Pope and is governed by the teachings of Jesus Christ, summarized in the New Testament of the Bible, as well as by the teachings of the catechism.
Origin of Catholicism
For Catholics, the origin of the Church dates back to the first century, when Jesus named Peter as “stone of the Church”, so they consider him the first of the Popes. After centuries of preaching and persecution, the emperor Theodosius made Christianity official through the edict of Thessalonica, promulgated in the year 380. From that moment on, the adjective “catholic” was used to describe the Church, which means “universal”. This appellation welcomed all the believing communities scattered in the domains of the Roman Empire.
What is the purpose of Catholicism?
The purpose of Catholicism, like that of all Christian currents, is the proclamation of the New Covenant and the salvation of souls. Catholicism teaches that the Church is a living body, made up of all believers, and that the purpose is to honor Christ through repentance of sins and conversion.
Doctrinal Foundations of Catholicism
The Catholic faith is based on the Apostles’ Creed like other Christian denominations. For this reason, he believes in the Triune God, in the resurrection of the dead, the forgiveness of sins, eternal life and in the community of believers.
In addition, he believes in transubstantiation (Eucharist), which is the conviction that the body and blood of Christ are present in the bread and wine of the Eucharist. He also believes in the mediation of the Virgin Mary and the saints. Add the dogma of the Immaculate Conception of the Virgin.
Sacraments of Catholicism
Within Catholicism there are seven sacraments or rites that are considered spiritual parallels with natural life:
- Baptism: it is a rite with which a new believer is incorporated into the Catholic faith and through which he or she accepts the New Covenant.
- Confirmation: rite of reaffirmation of baptismal faith.
- Eucharist: it is the Sunday (or daily) celebration of the life, death and resurrection of Jesus, shared in the consecrated Bread and Wine.
- Reconciliation: it is the process of repentance and reparation for sins.
- Marriage: it is the ceremony by which a man and a woman unite before God.
- Anointing of the sick: it is the anointing of the sacred oil to alleviate suffering and forgive the sins of the sick.
- Priestly order: it is the consecration to serve God actively through the priesthood.